1. Select industrial castor and wheels
The purpose of using industrial castor and wheels is to reduce labor intensity and improve work efficiency. Choose the right industrial castor and wheels according to the application method, conditions and requirements (convenience, labor saving, durability). Please consider the following points: A. Load-bearing weight: (1) Load-bearing weight calculation: T=(E+Z)/M×N:
T=weight carried by each caster E=weight of the transport vehicle Z=weight of the mobile stage M=effective load-bearing quantity of the wheel
(factors of uneven distribution of position and weight should be considered) (2) Effective load-bearing quantity of the wheel (M) is as shown in the figure below:
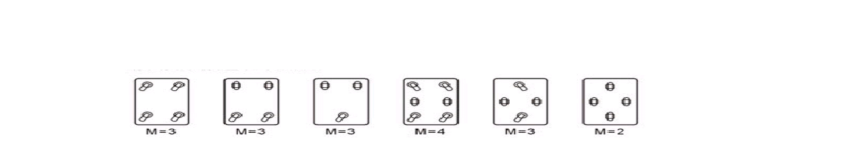
E=weight of the transport vehicle
Z=weight of the mobile stage M=effective load-bearing quantity of the wheel (factors of uneven distribution of position and weight should be considered) (2) Effective load-bearing quantity of the wheel (M) is as shown in the figure below:
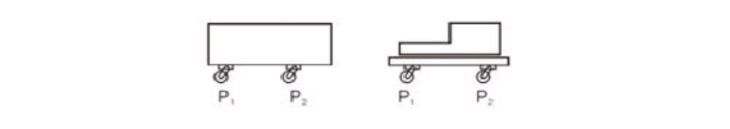
(3) When selecting the load-bearing capacity, calculate it according to the load-bearing capacity of the caster at the maximum support point. The caster support points are shown in the figure below, with P2 being the heaviest support point. B. Flexibility
(4) (1) industrial castor and wheels should be flexible, easy and durable. The rotating parts (caster rotation, wheel rolling) should be made of materials with low friction coefficient or accessories assembled after special processing (such as ball bearings or quenching treatment).
(5) (2) The larger the eccentricity of the tripod, the more flexible it is, but the load-bearing weight is correspondingly reduced.
(6) (3) The larger the diameter of the wheel, the less effort it takes to push it, and the better it can protect the ground. Larger wheels rotate slower than smaller ones, are less likely to heat up and deform, and are more durable. Choose wheels with larger diameters as much as possible under the conditions that the installation height allows.
(7) C. Moving speed: Caster speed requirements: Under normal temperature, on a flat ground, no more than 4KM/H, and with a certain amount of rest.
(8) D. Use environment: When selecting, the ground material, obstacles, residues or special environments (such as iron filings, high and low temperatures, acidity and alkali, oil and chemical practices, and places requiring anti-static electricity) should be considered. industrial castor and wheels made of special materials should be selected for use in special environments.
(9) E. Installation precautions: Flat top: The installation surface must be flat, hard and straight, and not loose. Orientation: The two wheels must be in the same direction and parallel. Thread: Spring washers must be installed to prevent loosening.
(10) F. Performance characteristics of wheel materials: Welcome to visit our company or request catalog information.
Introduction to performance test of industrial industrial castor and wheels
A qualified caster product must undergo strict quality and performance tests before leaving the factory. The following is an introduction to the five types of tests currently used by enterprises:
1. Resistance performance test When testing this performance, the caster should be kept dry and clean. Place the caster on a metal plate insulated from the ground, keep the wheel edge in contact with the metal plate, and load 5% to 10% of its standard load on the caster. Use an insulation resistance tester to measure the resistance value between the caster and the metal plate.
2. Impact test Install the caster vertically on the ground test platform, so that a 5kg noon falls freely from a height of 200mm, allowing a 3mm deviation to impact the wheel edge of the caster. If there are two wheels, both wheels should impact at the same time.
3. Static load test The static load test process of industrial castor and wheels is to fix the industrial castor and wheels on a horizontal and smooth steel test platform with screws, apply a force of 800N along the center of gravity of the industrial castor and wheels for 24 hours, remove the force for 24 hours and check the condition of the industrial castor and wheels. After the test, the deformation of the industrial castor and wheels measured does not exceed 3% of the wheel diameter, and the rolling, rotation around the axis or braking function of the industrial castor and wheels after the test is completed is qualified.
4. Reciprocating wear test The reciprocating wear test of industrial castor and wheels simulates the actual rolling conditions of industrial castor and wheels in daily use. It is divided into two types: obstacle test and no obstacle test. The industrial castor and wheels are properly installed and placed on the test platform. Each test caster is loaded with 300N, and the test frequency is (6-8) times/min. One test cycle includes a back and forth movement of 1M forward and 1M reverse. During the test, no caster or other parts are allowed to detach. After the test, each caster should be able to travel its normal function. After the test, the rolling, pivoting or braking functions of the caster should not be damaged.
5. Rolling resistance and rotation resistance test
For the rolling resistance test, the standard is to install three industrial castor and wheels on a fixed three-arm base. According to different test levels, a test load of 300/600/900N is applied to the base, and a horizontal traction is applied to make the caster on the test platform move at a speed of 50mm/S for 10S. Since the friction force is large and there is a speed at the beginning of the caster rolling, the horizontal traction is measured after 5S of the test. The size does not exceed 15% of the test load to pass.
The rotation resistance test is to install one or more industrial castor and wheels on a linear or circular motion tester so that their direction is 90° to the driving direction. According to different test levels, a test load of 100/200/300N is applied to each caster. Apply a horizontal traction force to make the caster on the test platform travel at a speed of 50mm/S and rotate within 2S. Record the maximum traction force that makes the caster rotate. If it does not exceed 20% of the test load, it is qualified.
Note: Only products that have passed the above tests and are qualified can be identified as qualified caster products, which can play a greater role in different application fields. Therefore, each manufacturer should attach great importance to the post-production testing link.
Post time: Jan-13-2025