Castors are a general term, including movable castors, fixed castors and movable castors with brake. The movable castors, also known as universal wheels, allow 360 degrees of rotation; Fixed castors are also called directional castors. They have no rotating structure and cannot rotate. Generally, the two castors are used together. For example, the structure of the trolley is two directional wheels at the front and two universal wheels near the push handrail at the rear. Castors are made of various materials, such as pp castors, PVC castors, PU castors, cast iron castors, nylon castors, TPR castors, iron-core nylon castors, iron-core PU castors, etc.
1. Structural characteristics
Installation height: refers to the vertical distance from the ground to the equipment installation position, and the installation height of castors refers to the maximum vertical distance from the castor base plate and the wheel edge.
Steering center distance of support: refers to the horizontal distance from the vertical line of the center rivet to the center of the wheel core.
Turning radius: refers to the horizontal distance from the vertical line of the central rivet to the outer edge of the tire. The proper spacing enables the castor to turn 360 degrees. Whether the rotation radius is reasonable or not will directly affect the service life of the castors.
Driving load: the bearing capacity of castors when moving is also called dynamic load. The dynamic load of castors varies according to the different test methods in the factory and the different materials of wheels. The key is whether the structure and quality of the support can resist impact and shock.
Impact load: the instantaneous bearing capacity of castors when the equipment is impacted or vibrated by the load. Static load static load static load static load: the weight that castors can bear under static state. Generally, the static load shall be 5~6 times of the running load (dynamic load), and the static load shall be at least 2 times of the impact load.
Steering: Hard and narrow wheels are easier to turn than soft and wide wheels. Turning radius is an important parameter of wheel rotation. If the turning radius is too short, it will increase the difficulty of turning. If it is too large, it will cause the wheel to shake and shorten its life.
Driving flexibility: The factors that affect the driving flexibility of castors include the structure of the support and the selection of the support steel, the size of the wheel, the type of the wheel, the bearing, etc. The larger the wheel, the better the driving flexibility. The hard and narrow wheels on the smooth ground are more labor-saving than the flat soft wheels, but the soft wheels on the uneven ground are labor-saving, but the soft wheels on the uneven ground can better protect the equipment and shock absorption!
2. Application area
It is widely used in handcart, mobile scaffold, workshop truck, etc.
Castors are mainly divided into two categories:
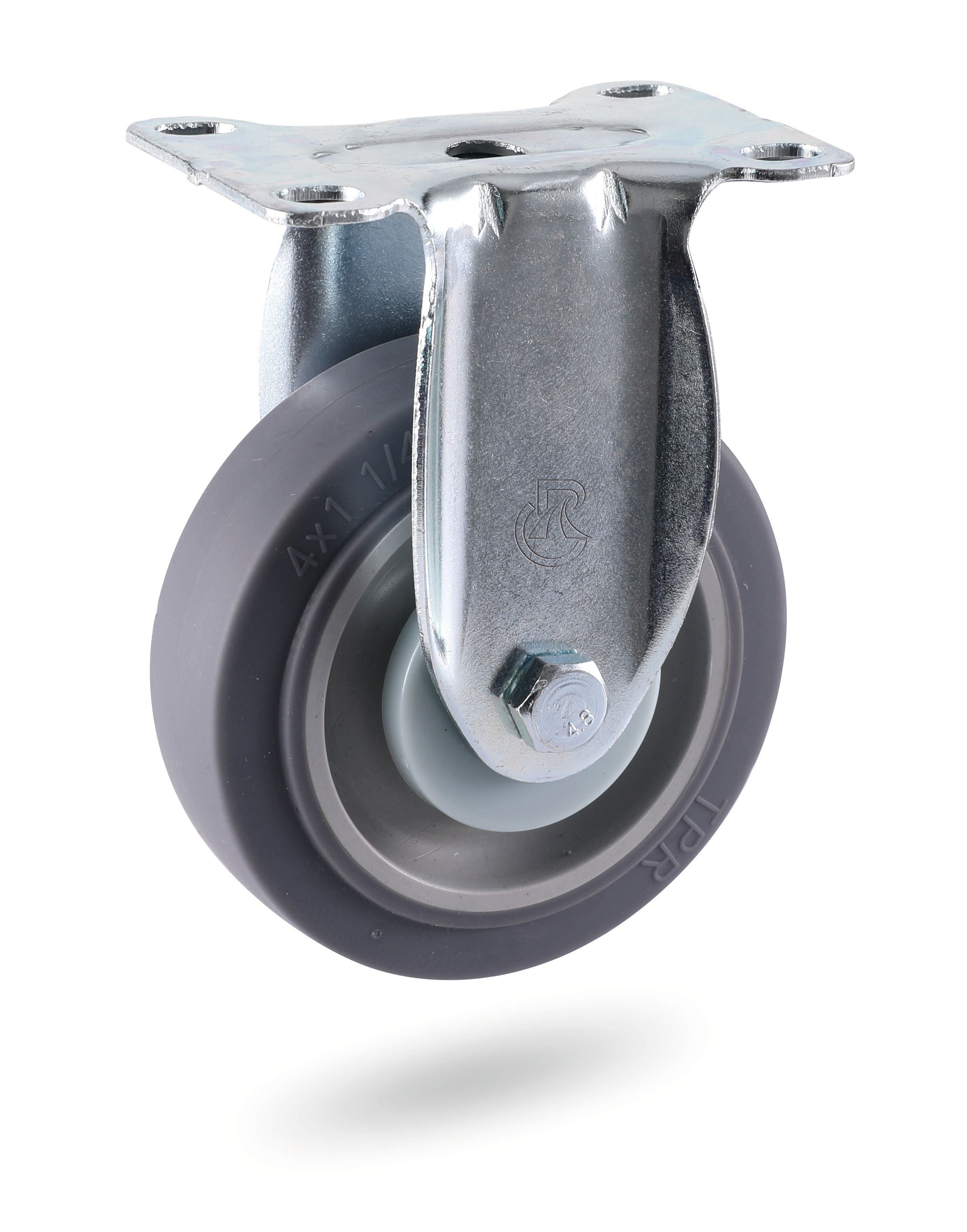
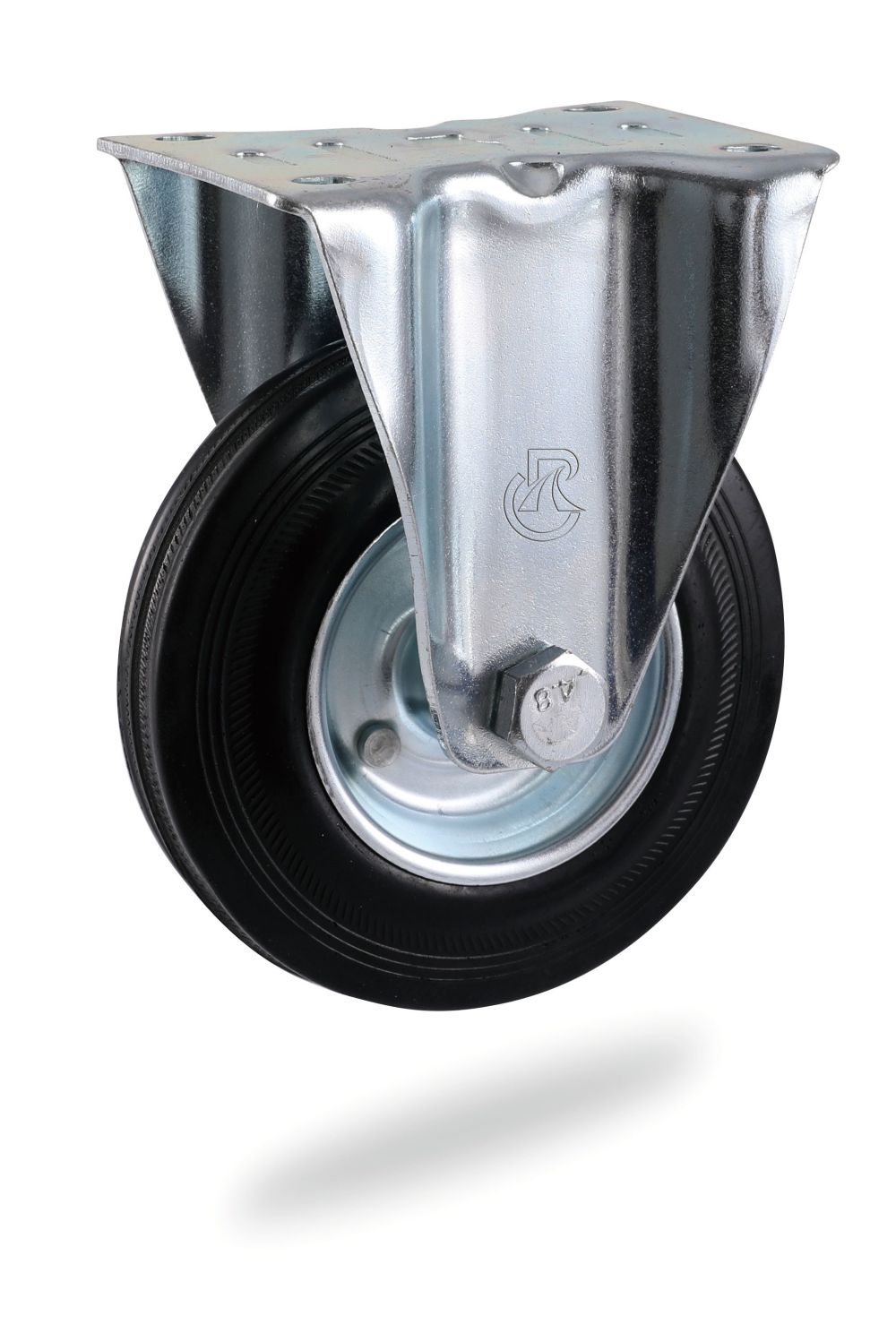
A. Fixed castors: the fixed bracket is equipped with a single wheel, which can only move in a straight line.

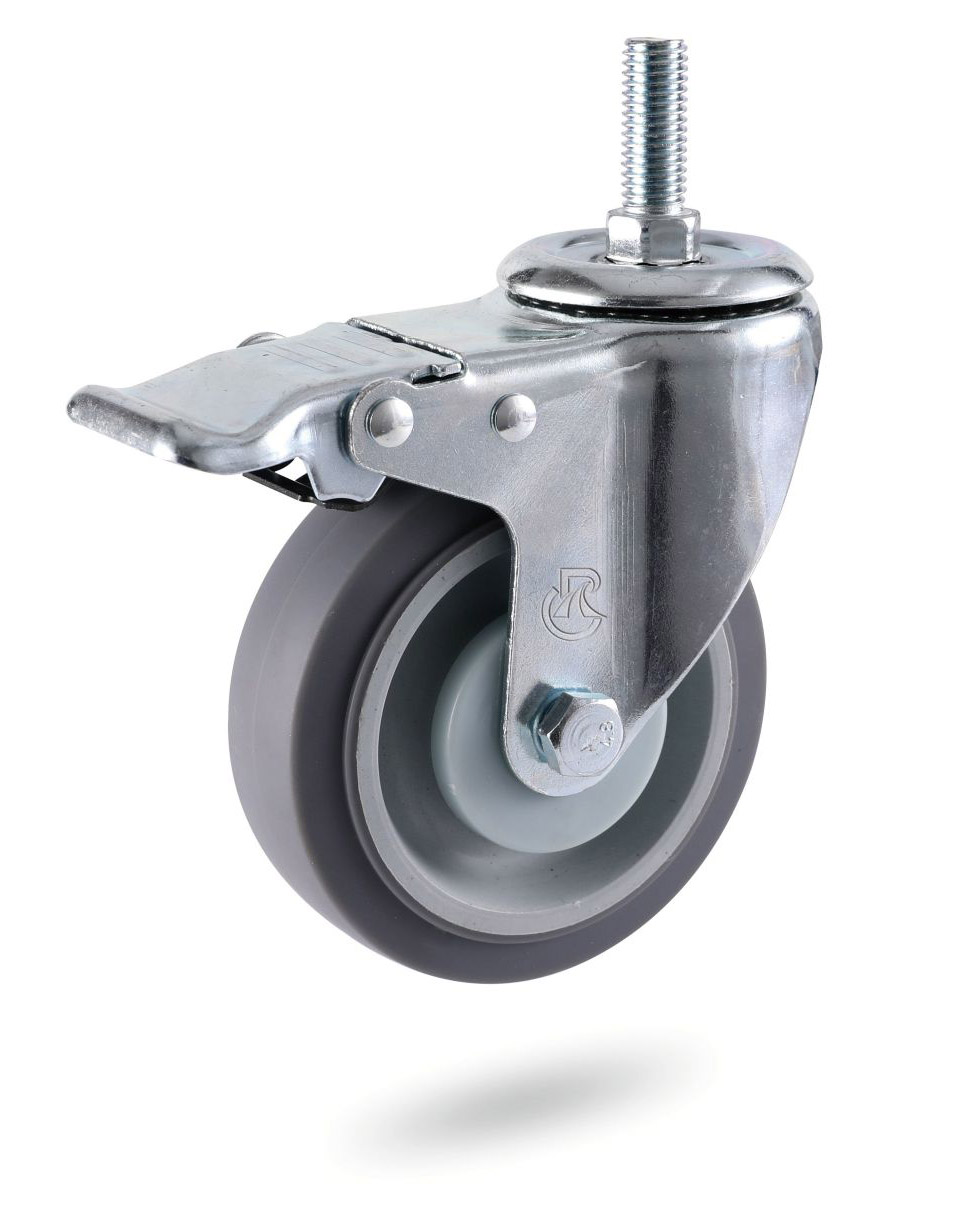
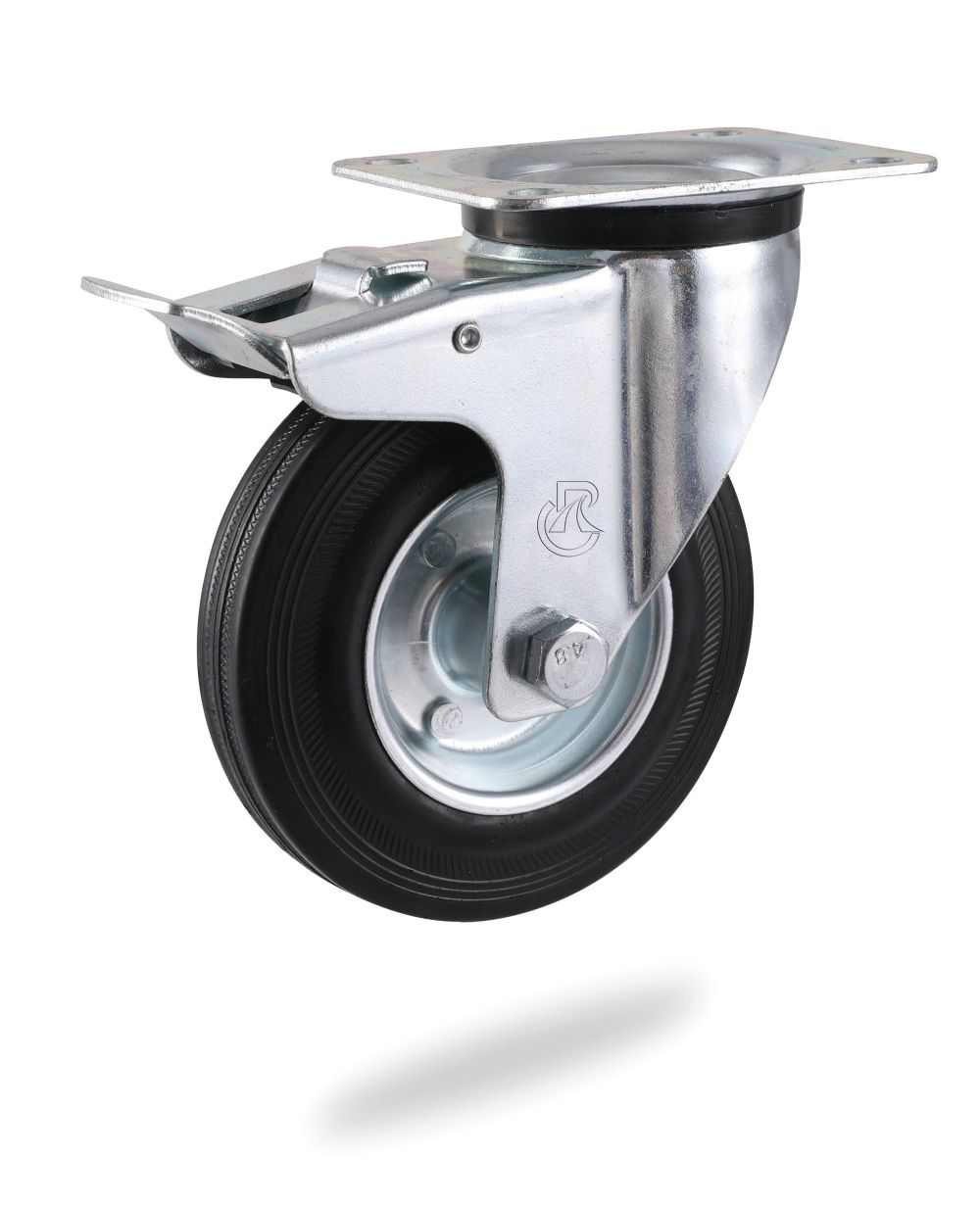
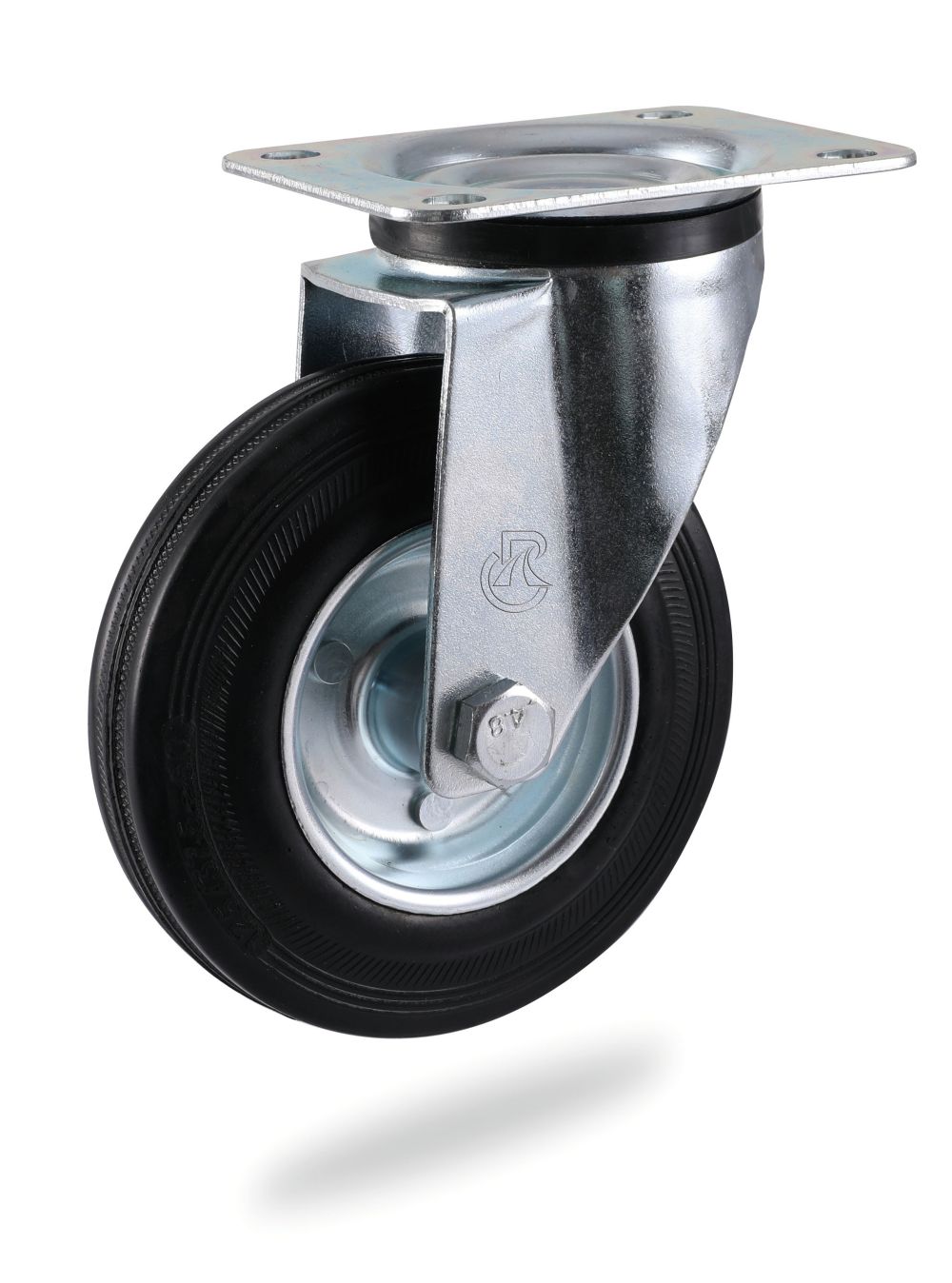
B. Movable casteors: the bracket with 360 degree steering is equipped with a single wheel, which can drive in any direction at will.
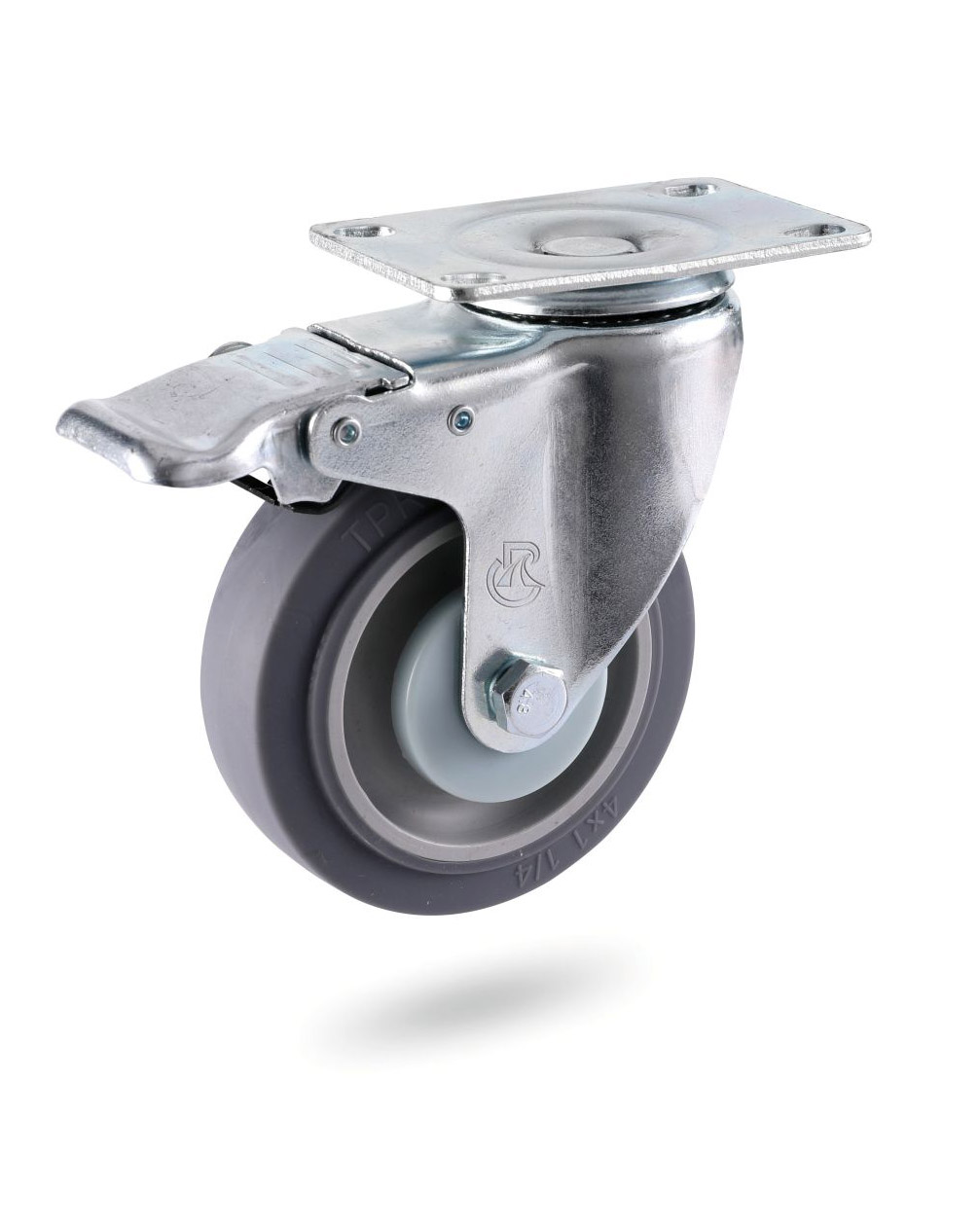
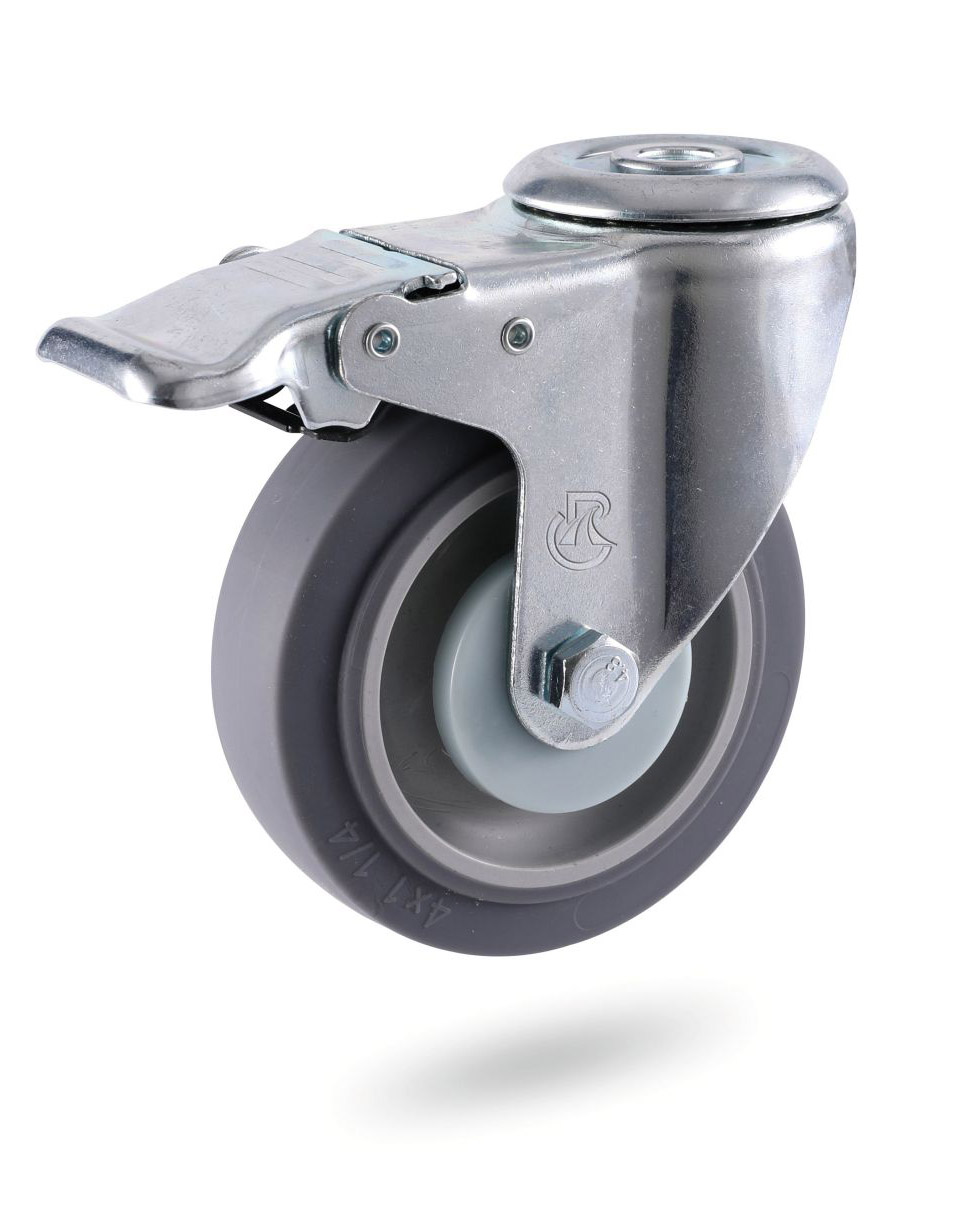
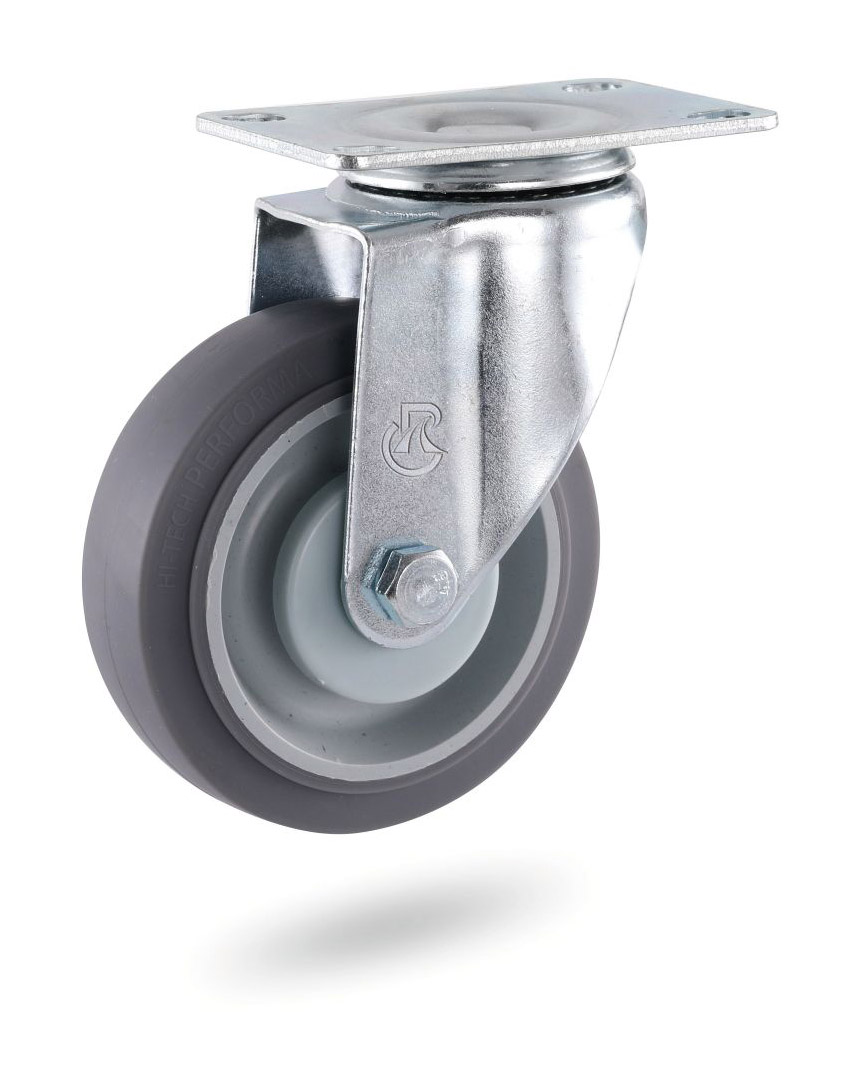




Castors have a wide variety of single wheels, which vary in size, model, tire tread, etc. Select the appropriate wheel based on the following conditions:
A. Use site environment.
B. Load capacity of the product.
C. The working environment contains chemicals, blood, grease, oil, salt and other substances.
D. Various special climates, such as humidity, high temperature or severe cold
E Requirements for impact resistance, collision resistance and driving tranquility.
3. Material quality
Polyurethane, cast iron steel, nitrile rubber (NBR), nitrile rubber, natural rubber, silicone fluororubber, neoprene rubber, butyl rubber, silicone rubber (SILICOME), EPDM, Viton, hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR), polyurethane rubber, rubber, PU rubber, PTFE rubber (PTFE processing parts), nylon gear, Polyoxymethylene (POM) rubber wheel, PEEK rubber wheel, PA66 gear.
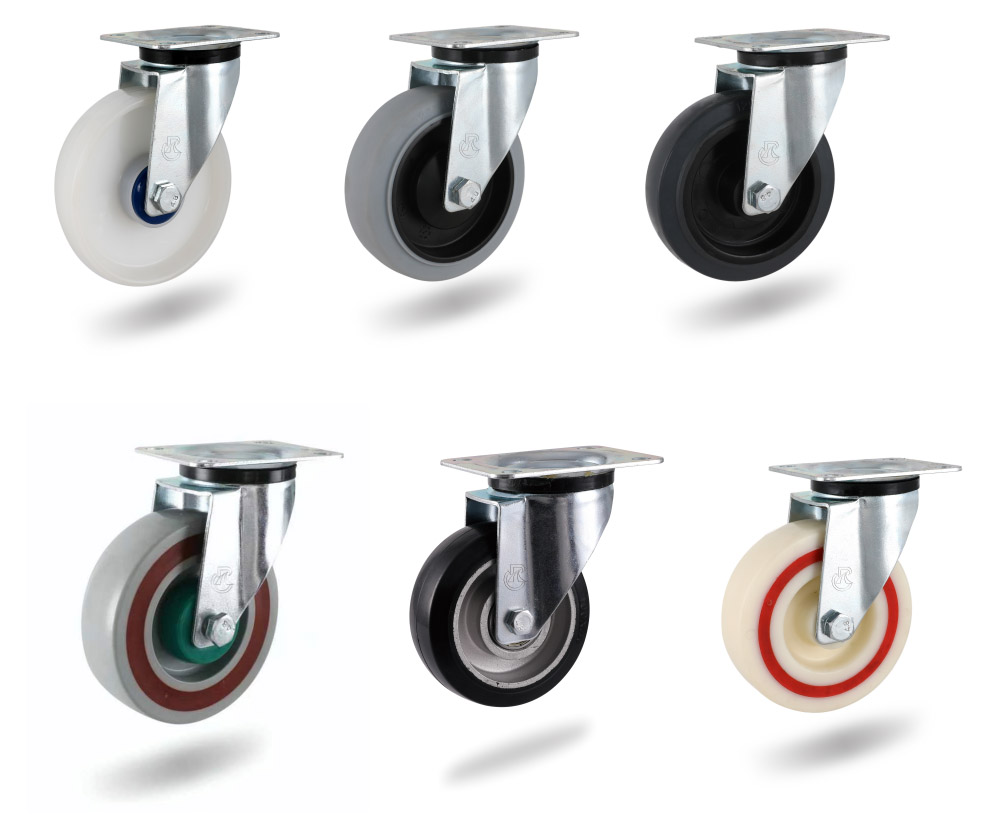

4. Application industry
Industrial, commercial, medical equipment and machinery, logistics and transportation, environmental protection and cleaning products, furniture, electrical appliances, beauty equipment, mechanical equipment, craft products, pet products, hardware products and other industries.

5. Wheel selection
(1). Select the wheel material: first, consider the size of the road surface, obstacles, residual substances (such as iron filings and grease) on the site, the environmental conditions (such as high temperature, normal temperature or low temperature) and the weight that the wheel can carry to determine the appropriate wheel material. For example, rubber wheels cannot be resistant to acid, grease and chemicals. Super polyurethane wheels, high-strength polyurethane wheels, nylon wheels, steel wheels and high-temperature wheels can be used in different special environments.
(2). Calculation of load capacity: in order to calculate the required load capacity of various castors, it is necessary to know the dead weight of the transport equipment, the maximum load and the number of single wheels and castors used. The required load capacity of a single wheel or castor is calculated as follows:
T=(E+Z)/M × N:
---T=required bearing weight of single wheel or castors;
---E=dead weight of transport equipment;
---Z=maximum load;
---M=number of single wheels and castors used;
---N=safety factor (about 1.3-1.5).
(3). Determine the size of wheel diameter: generally, the larger the wheel diameter is, the easier it is to push, the larger the load capacity is, and the better it is to protect the ground from damage. The selection of wheel diameter size should first consider the weight of the load and the starting thrust of the carrier under the load.
(4). Selection of soft and hard wheel materials: generally, the wheels include nylon wheel, super polyurethane wheel, high-strength polyurethane wheel, high-strength synthetic rubber wheel, iron wheel and air wheel. Super polyurethane wheels and high-strength polyurethane wheels can meet your handling requirements no matter whether they are driving on the ground indoors or outdoors; High-strength artificial rubber wheels can be used for driving on hotels, medical equipment, floors, wooden floors, ceramic tile floors and other floors that require low noise and quiet when walking; Nylon wheel and iron wheel are suitable for places where the ground is uneven or there are iron chips and other substances on the ground; The pump wheel is suitable for light load and soft and uneven road.
(5). Rotation flexibility: the larger the single wheel turns, the more labor-saving it will be. The roller bearing can carry a heavier load, and the resistance during rotation is greater. The single wheel is installed with high-quality (bearing steel) ball bearing, which can carry a heavier load, and the rotation is more portable, flexible and quiet.
(6). Temperature condition: severe cold and high temperature conditions have a great impact on the castors. The polyurethane wheel can rotate flexibly at a low temperature of minus 45 ℃, and the high-temperature resistant wheel can rotate easily at a high temperature of 275 ℃.
Special attention: because three points determine a plane, when the number of castors used is four, the load capacity should be calculated as three.
6. Wheel frame selectioner industries.



7. Bearing selection
(1) Roller bearing: the roller bearing after heat treatment can bear heavy load and has general rotation flexibility.eavy load and has general rotation flexibility.

(2) Ball bearing: The ball bearing made of high-quality bearing steel can bear heavy load and is suitable for occasions requiring flexible and quiet rotation.

(3) Plain bearing: suitable for high and ultra-high load and high speed occasions

Post time: Feb-17-2023